Interfacing with Technology Trends in Touching Less

Seven years on from the launch of the Amazon Alexa, we are still finding our way into touchless control of hardware and software. Voice technology has matured, and so has our understanding of when and how to use it. Other touchless solutions are now emerging and provide options in many situations. Implementing these new solutions and seeking acceptance and adoption from users is key to the evolution of touchless interfaces.
The Changing Landscape of Touchless Technology
Touchless technology allows users to control systems and devices without physical contact. In a post-pandemic world, audio-visual (AV) manufacturers are using existing and new technologies to create solutions that can help people return safely to public facilities like offices, hospitals, schools, hotels, and restaurants. The 2020 estimate for the gesture recognition and touchless sensing market was around 23.6 billion US dollars.
Like AV manufacturers, AV system integrators are also thinking creatively. Integrators are combining multiple technologies to create more holistic solutions for their clients. They are designing touchless systems to automate door access, control meeting room equipment, and manage lighting, video, and digital signage.
Here are a few noticeable trends in touchless experiences:
QR Code and BYOD Control Apps
Shared screens, buttons, and remote controls are popular control mechanisms for building management systems. But shared devices spread germs, and they are vulnerable to vandalism, theft, and displacement. So, AV manufacturers and system integrators are harnessing the power of QR codes, custom apps, and bring-your-own-device (BYOD) philosophy to build touchless AV systems. These systems require minimal infrastructure investment.
Mobile apps, phone cameras, and wearable devices are replacing shared control devices. For example, A QR code can be placed in the room in printed form and displayed on one of the screens. Users can download an app on their devices and scan the QR code to gain control of the meeting room equipment. It eliminates the need for touching the equipment controls to activate the screens, microphones, and cameras. Crestron One and Atlona Velocity are examples of QR-based BYOD control.
Touchless Access Control
Public facilities require access control for physical and digital security. But keycard-based access control adds a lot of bureaucracy. Issuing keycards to employees and visitors takes up time and resources.
Mobile app-based access control systems are faster and more efficient. Multifamily, commercial, and office spaces can use the apps to issue visitor permits, log visitation information, and track arrivals and departures. The systems can be enhanced using face recognition technology. A robust software-based access control solution automates the processes and decreases security errors. No more dangling keycards that someone forgot to deactivate.
Voice-Controlled Scheduling Systems
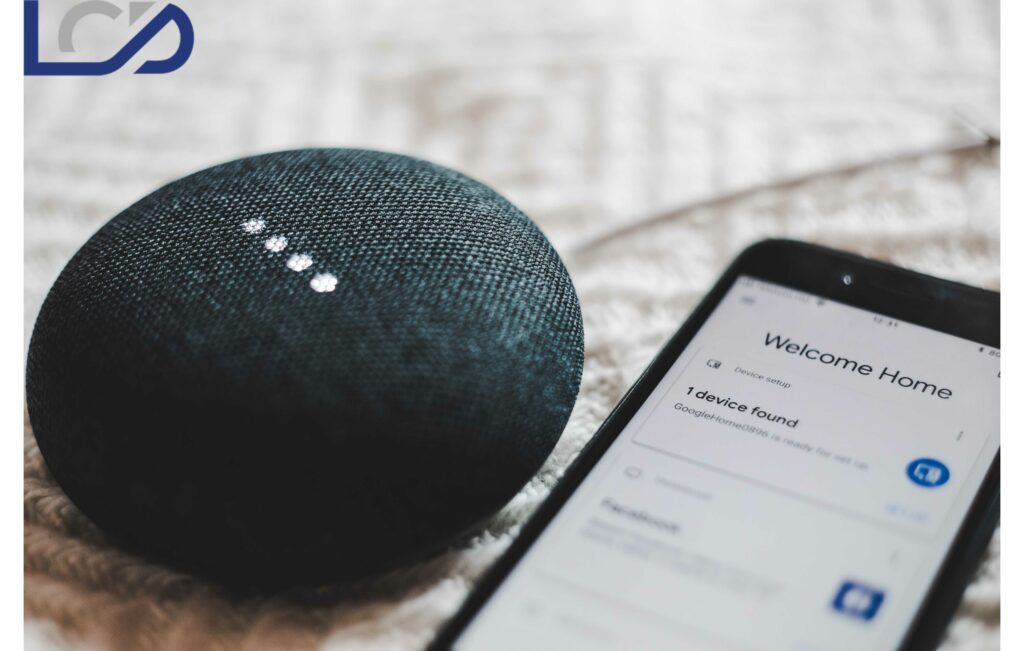
Digital assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Home are crossing over to commercial applications. Businesses are using these voice technologies to install AV systems that respond to scheduling requests. Whether users want to book a conference room or connect to a remote location during a meeting, voice assistants are becoming part of modern enterprise infrastructure. AV Integrators are installing voice controllers in conference rooms and shared public spaces. The no-touch automation of scheduling tasks is providing a better user experience for AV customers.
AirPlay for Touchless Content Sharing
Apple AirPlay has made video streaming, screen mirroring, and file sharing easier over wireless connections. Meeting attendants can share content without using a dongle or a wired device. Also, users are already acquainted with the AirPlay user interface. So, familiarity has led to more customers using touchless content sharing.
For AV integrators, wireless and touchless content sharing has simplified equipment installation and maintenance. Integrators have fewer wired connections and proprietary software to consider. It has decreased their workloads and freed up resources.
Evolution of Audio Control with Alexa and Other Voice Assistants
Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Home are becoming central control systems for enterprises and small businesses. Voice assistants started as simple audio search engines, and they were initially useful only for digital information queries. But, they have entered the realm of the physical world with the help of the Internet of Things (IoT).
Today voice assistants have become a crucial part of controlling smart homes and offices. With voice assistants, users can control lighting, elevators, conferencing systems, digital displays, security cameras, door locks, and more. Voice technology providers let organizations integrate custom AV control systems through application programming interfaces (APIs) and software development kits (SDKs).
The Impact of Voice Assistants In the Professional AV Environment
For AV integrators, voice technology has changed the design, installation, and implementation of AV systems. Initially, AV integrators assumed voice assistant integration would require more proprietary hardware and software installations. However, as the technology matures and more wireless and IoT-based solutions come into the market, voice assistant technology makes AV integration easier.
AV manufacturers are using Amazon Alexa, Google Home, and Google Nest as an integral part of their design. It is leading to more standardized solutions and opening new opportunities. AV integrators can use the standard APIs and SDKs to design customized solutions compatible with multiple AV vendors.
Touchless Solutions for Assistive Technology
A side benefit of touchless user interfaces is that the solutions provide more accessibility. Disabled people can use voice-activated controls to open doors, turn on lights, or activate and control AV equipment.
The Future of Touchless Solutions
Touchless technology has come a long way. But it is still an evolving field. New and exciting developments are already on the horizon. Here are a few things that might be interesting:
- Motion Capture and Gesture Recognition: Advanced motion sensors will make it easier to control AV environments without any additional control devices. It might remove the necessity for BYOD devices. Combining voice recognition, face recognition, and gesture control will make the new systems true touchless experiences.
- Mind-Controlled Interface: Scientists are developing brain-computer interfaces. These interfaces will allow users to issue commands without using voice technology. It will open new avenues for no-touch applications.
- Haptic Interface: A challenge of using touchless technology is the absence of touch. Our brains have a difficult time understanding objects without tactile sensations. Haptic interface generates the feeling of touch, allowing users to manipulate objects more accurately. Imagine drawing on-screen using your fingers and having more tactile feedback during the process.
Touchless technology has already transformed the AV industry, and we can expect more innovations to bring better solutions in the future. If you want to learn more about implementing touchless technology and our consultancy services, please feel free to contact us today.